
Metals have played a pivotal role in the progress of human civilization, from the Bronze Age to the contemporary era of advanced technology. Among the myriad of metals, two primary categories stand out: ferrous and non-ferrous. Understanding the distinctions between these two is crucial not only for metallurgists and engineers but also for anyone intrigued by the fascinating world of materials science. If you want to learn about metals, like how strong steel is or how well aluminium conducts electricity, the best way to do it is through science tuition. It’s like going on a learning adventure with a guide who helps you understand these things better.
Properties and Characteristics of Ferrous Metals
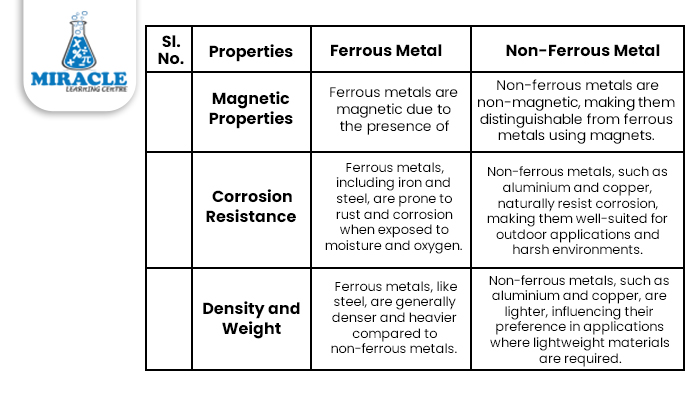
Ferrous metals are widely recognized for their exceptional strength and durability. These metals exhibit magnetic properties due to the presence of iron. One of the key characteristics of ferrous metals is their high tensile strength, which makes them resistant to deformation and capable of withstanding heavy loads. Additionally, ferrous metals have excellent heat conductivity, making them suitable for applications requiring high-temperature resistance.
Common examples of ferrous metals include iron, steel, and cast iron. Iron is the most abundant metal on Earth and is widely used in construction, infrastructure, and manufacturing industries. Steel, a versatile alloy of iron and carbon, is highly valued for its strength, making it an essential material in the automotive, aerospace, and machinery sectors. Cast iron, known for its excellent heat retention and wear resistance, is commonly used in the production of engine blocks, pipes, and cookware.
Ferrous metals find applications in various industries. In the construction sector, steel is extensively used for structural applications, such as beams, columns, and reinforcement bars. The automotive industry relies on ferrous metals for manufacturing components like engine blocks, chassis, and body panels. In the manufacturing sector, ferrous metals play a crucial role in the production of machinery, tools, and equipment.
Properties and Characteristics of Non-Ferrous Metals
Non-ferrous metals are distinct from ferrous metals as they do not contain iron and are non-magnetic. These metals possess unique properties that make them highly desirable for specific applications. One key characteristic of non-ferrous metals is their excellent electrical conductivity.
This property makes them indispensable in electrical and electronic systems. Additionally, non-ferrous metals are known for their lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
There are several examples of non-ferrous metals, including aluminium, copper, zinc, lead, and tin. Aluminium, known for its lightness and strength, is extensively used in the aerospace industry, as well as in the production of automotive parts and packaging materials. Copper, an excellent conductor of electricity and heat, is widely used in electrical wiring, plumbing, and telecommunications. Zinc is valued for its anti-corrosive properties and is commonly used in galvanizing steel to protect it from rusting.
Non-ferrous metals find applications in various industries. In the electrical industry, copper is extensively used for wiring, power distribution, and electrical equipment. Aluminium is used in the construction of aircraft, automobiles, and packaging materials. Zinc is essential in the production of batteries, alloys, and corrosion-resistant coatings.
Differences Between Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Metals
While both ferrous and non-ferrous metals have their unique properties and applications, there are several key differences between them.
Properties Ferrous Metals Non-Ferrous Metals
Conclusion
The distinctions between ferrous and non-ferrous metals are fundamental to understanding the properties and applications of different materials. Whether you are a student aspiring to become a metallurgist or someone with a keen interest in the world of metals, a solid foundation in science education is essential.
To navigate the complexities of metallurgy effectively, consider enrolling in a science tuition centre. The guidance and expertise provided by a knowledgeable tutor, especially from Miracle Learning Centre, can make the learning process more engaging and fruitful. As we continue to advance in technology and industry, a deep understanding of materials science becomes increasingly valuable, making science tuition a wise investment in one’s educational journey